
Recently, ESN hosted a webinar on Cultivating Mental Health in Grad School in response to the mental health crisis evident in universities and our wider society that has been exacerbated by COVID-19. We are grateful to Grace Chung and Cahleen Shrier for this two part series addressing this crisis and the distinctive hope we have as followers of Christ
I. Introduction
Millennials have had an increase in diagnoses of depression since 2013 (Blue Cross, 2019). Some individuals suffering from depression have a compromised frontal lobe, the part of the brain in charge of cognitive decisions and impulse control. Because of this, depressed individuals are more likely to turn to alcohol leading to substance abuse and addiction (Skóra, 2020). In addition, other harmful habits can also develop, for example, overeating. During the pandemic, there was an increase in liquor store purchases, frozen food purchases and weight gain. We will look at the biological and psychological aspects of depression in Part 1.
Biological, psychological, social, and spiritual components of life influence us; they shape mental and physical health. As Christians, the Bible instructs individuals on how to think about God’s truths, leading to a renewed mind. This renewed mind then allows individuals to make good decisions and eventually create good habits. The biological issues Millennials are facing emphasize the importance of strengthening spiritual health and replacing negative thoughts with those that are hopeful. Part 2 will explore the hope that is provided in Christianity.
II. Prevalence
Depression has been increasing among Millennials since the early 2000s. From 2013 to 2021, there was a 47% increase in major depression diagnosis overall. However, the increase is greater in teens and Millennials (Fig 1; Blue Cross, 2019).

Figure 1. “Major depression diagnoses are increasing faster in Millennials and teens . . . “ (Blue Cross, 2019)
In the height of the 2021 COVID-19 pandemic, depression diagnoses continued to increase. Depression involves feelings of deep pain, anger, frustration, and loneliness. These feelings prevent an individual from functioning fully in their life. Biologically, it is multifaceted and can include chemical imbalances in the brain in about half of the individuals diagnosed with depression (Ruiz, 2018).
III. Negative Bias
Significantly higher levels of depressive symptoms ​are associated with greater amounts of automatic negative thoughts (Clark, 2009). Though negative thoughts do not necessarily cause depression, they can affect the symptoms ​that depressed individual’s experience. The more the negative thought pathway is practiced, the more that route is ingrained in ​the brain.
This is similar to a pathway in a forest. If you walk it once, your footprints will not last. However, if you walk the pathway consistently your footprints will leave a path. Neural pathways function just like this. While all individuals have this negativity bias, people who are depressed suffer from higher levels of negative thinking due to depression (Vaish, 2008). Therefore, depressed individuals practice this negative thought pathway more than non-depressed individuals, which further ingrains this as a powerful, default neural pathway.
IV. Altered Brain Function
Optimal brain development and brain health provides for moments of elevated mood. The frontal lobe is the part of the brain that is the main center for behavior, emotion, and even personality. In addition, the limbic system is involved in the control of reactions to stress, while it also controls emotions, behavior, and personality. Therefore, weakness or damage to these areas results in a change in personality, emotion, and behavior.
A damaged or weakened frontal lobe occurs in depressed individuals. This along with several other regions of the brain causes the brain to be compromised (Ruiz, 2018). Furthermore, a weakened frontal lobe is part of the problem that creates bad habits due to decreased cognitive ability and absence of impulse control (Johnson, 2009). For example, a weakened orbital frontal lobe is correlated to chronic alcohol abuse (Moorman, 2018).
Damage to gray matter in depression-associated areas of the brain, including the frontal lobe, was found in depressed patients (Z. Li, 2021). The developing frontal lobe and weaker brain areas coupled with depression can lead individuals to substance abuse. This was evident during the COVID-19 pandemic; there was a 60 percent increase in drinking alcohol across the U.S. in general (Grossman, 2020) and an increase in liquor sales (Fig. 2; Castaldelli-Maia, 2021).
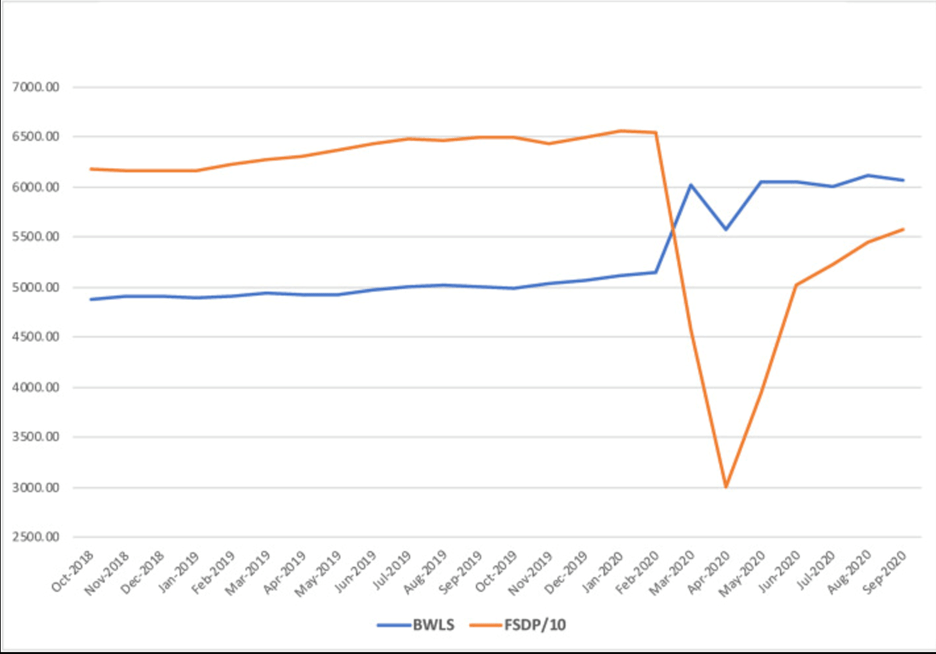
Figure 2. “Beer, Wine and Liquor (BWLS) and Food Services and Drinking Places (FSDP) retail sales in the U.S., 2018-2020 (in million US dollars).” (Castaldelli-Maia, 2021)
V. Impulsivity
Part of the reason for seeing such dramatic increases in alcohol sales is due to a lack of impulse control. Normal brain development of the frontal lobe is completed by about twenty-five years old (Gavin, 2009). This part of the brain is involved in processing information and impulse control. It is damaged in depressed individuals (Johnson, 2009) and can lead to impulsivity. Impulsivity causes decreased self-reflection, rapid, risky decision-making and less inhibition of certain behaviors (Skóra, 2020).
Lacking impulse control can lead to physical and psychological dependence on alcohol (Fig. 3). This poor behavior continues in a downward cycle as long-term substance abuse leads to a damaged frontal lobe, thus making an individual more likely to keep participating in alcohol abuse (Uhl, 2019). With this in mind, one can better understand why statistics for drug and alcohol-induced deaths among 18 to 34-year-olds increased from 2007-2017; drug-related deaths increased 108 percent and alcohol-induced deaths increased 69 percent (Farberman, 2019).
VI. Addiction
Addiction has a cycle with three stages: intoxication, withdrawal, and preoccupation. Substance abuse involves neuroadaptation; the neurons adapt to the environment that they are in (Uhl, 2019).
It starts with the intake of alcohol, which can lead to binging and intoxication. After binging, the individual suffers from withdrawal symptoms, which leads to preoccupation and anticipation for the next binge. Withdrawal leads to stress and reward behaviors which will change the neural pathways in the brain. The neural pathway efficiency then decreases in response to alcohol which causes a biological change resulting in a higher dependence on alcohol (Uhl, 2019). This ultimately leads to dependence through a continued binge, withdrawal, adaptation and anticipation cycle (Fig. 3).
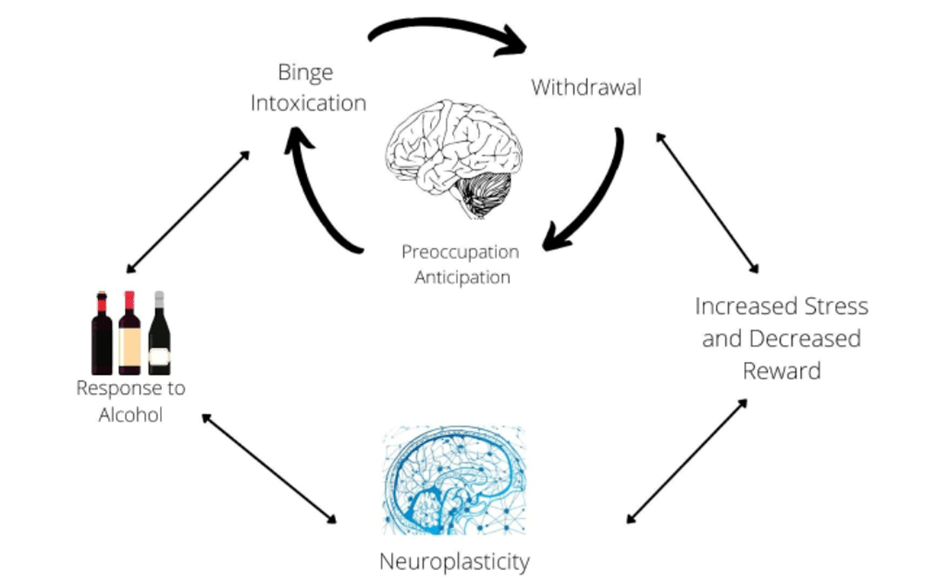 Fig. 3. Adapted from Wise and Koob, 2014.
Fig. 3. Adapted from Wise and Koob, 2014.
VII. Nutrition
While a weak frontal lobe can lead to alcohol and drug abuse, it can also lead to poor eating habits. According to the American Psychological Association, 42 percent of U.S. adults reported they had undesired weight gain during the Covid-19 quarantine. The average weight gain was 29 pounds (Weir, 2021)! For the Millennial generation specifically, there was a 41-pound weight gain in 48 percent of individuals who expressed they had undesired weight gain. Gaining this much weight can pose serious health risks such as Type II Diabetes and even ischemic stroke (American Psychological Association, 2020).
The main cause of overeating was stress. During the pandemic, Millennials were stressed about the COVID-19 pandemic, work, financial issues and even the future of the nation (American Psychological Association, 2020). The stress response in the body uses the hormone, cortisol and increased cortisol can lead to an increased appetite. To feel better about the stress, people sometimes turn to comfort foods which can lead to weight gain (van der Valk, 2018). During the pandemic, frozen food purchases increased by 21 percent compared to the previous year (American Frozen Food Institute, 2021). Many frozen foods are highly processed and unhealthy.
Weight gain among individuals is correlated to suffering from depression (Block, 2009). Eating unhealthy foods leads to weight gain and the risk of depression. New studies continue to associate diet with depressive symptoms. A healthy diet consisting of higher intakes of fruits, vegetables, fish and whole grains led to a 30 percent reduced risk for depression and decreased depressive symptoms in adults (Jacka, 2017). However, a typical western diet, low in vegetables and fruits and high in dairy products and red meats, is associated with an increased risk of depression (Y. Li, 2017).
VIII. Exercise
Not only is diet important, but so is exercise. During the beginning of the pandemic in 2020, gyms were temporarily closed. Individuals were no longer motivated to exercise, because they lost their gym partner or gym community. Being social creatures, the individuals who surround us greatly impact our motivation, self-esteem, physical health, and psychological health (Kaur, 2020). Those who were exercising indoors during the pandemic reported having good mental health compared to individuals who were not working out. Furthermore, individuals exercising outdoors reported having excellent mental health (Colley, 2020). Exercising outdoors benefits mental health, because Vitamin D is produced in the body in response to sun exposure. Having low levels of Vitamin D is associated with the risk of depressive symptoms and the risk of developing obesity, liver disease, and gastrointestinal malabsorption (Coelin, 2021).
During the COVID-19 quarantine, the struggle to exercise and increased screen time led to poorer perceived mental health (Colley, 2020). Spending more time in front of a screen led to more isolation and less social interaction. Therefore, Millennials were cut off from an environment that provided them with motivation and a reason to exercise and go outside.
IX. Conclusion
Depression diagnoses have greatly increased in Millennials. The quarantine for COVID-19 escalated this by providing an optimal environment for depression to flourish: decreased exercise, decreased sunlight exposure, decreased nutrient rich foods, increased stress and increased worries. It makes sense that the brain and psychological health of Millennials suffered significantly during the pandemic.
The biological, psychological, social and spiritual components of depression require a complex approach to therapy. Conventional treatment addresses the bio-psycho-social aspects, but often leaves the spiritual piece untouched. When it does, it is superficial and often does not connect with a patients’ spiritual values. Part 2 will explore how connecting with Christian beliefs can provide hope for those with depression.
References
- American Frozen Food Institute. 2021. “Frozen Foods Are a Pandemic Powerhouse.” https://affi.org/frozen-foods-are-a-pandemic-powerhouse/.
- American Psychological Association. 2020. “Stress in America 2020: A National Mental Health Crisis.” https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2020/report-october.
- Block, Jason P., Yulei He, Alan M. Zaslavsky, Lin Ding and John Z. Ayanian. 2009. “Psychosocial Stress and Change in Weight Among US Adults.” American Journal of Epidemiology 170 (2): 181-92. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp104.
- Blue Cross Blue Shield. 2019. “Two Million Commercially Insured Americans Diagnosed with Major Depression Are Not Seeking Any Treatment.” https://www.bcbs.com/the-health-of-america/articles/two-million-commercially-insured-americans-diagnosed-major-depression-not-seeking-treatment.
- Ceolin, Gilciane, Giulia Pipolo Rodrigues Mano, Natália Schmitt Hames, Luciana da Conceição Antunes, Elisa Brietzke, Débora Kurrle Rieger and Júlia Dubois Moreira. 2021. “Vitamin D, Depressive Symptoms and Covid-19 Pandemic.” Frontiers in Neuroscience 15: 513. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.670879.
- Clark D, Goosen T. 2009. “The mediating effects of coping strategies in the relationship between automatic negative thoughts and depression in a clinical sample of diabetes patients.” Personality and Individual Differences. 2009;46:460-464. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2008.11.014.
- Colley, Rachel C., Tracey Bushnik and Kellie Langlois. 2020. “Exercise and Screen Time during the COVID-19 Pandemic.” Health Reports 31 (6): 3-11. https://doi.org/10.25318/82-003-x202000600001-eng.
- Farberman, Rhea K. 2019. “Pain in the nation: building a national resilience strategy: alcohol and drug misuse and suicide and the millennial generation : a devastating impact.” Trust for America’s Health, Washington, DC. http://resource.nlm.nih.gov/101751522
- Gavin L, MacKay AP, Brown K, Harrier S, Ventura SJ, Kann L, Rangel M, Berman S, Dittus P, Liddon N, Markowitz L, Sternberg M, Weinstock H, David-Ferdon C, Ryan G. 2009. “Sexual and reproductive health of persons aged 10-24 years – United States, 2002-2007.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). MMWR Surveill Summ. 2009 Jul 17;58(6):1-58. PMID: 19609250.
- Grossman, E. R., Benjamin-Neelon, S. E., & Sonnenschein, S. 2020. Alcohol Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Survey of US Adults. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(24), 9189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249189
- Jacka, Felice N., Adrienne O’Neil, Rachelle Opie, Catherine Itsiopoulos, Sue Cotton, Mohammedreza Mohebbi, David Castle, et al. 2017. “A Randomised Controlled Trial of Dietary Improvement for Adults with Major Depression (the ‘SMILES’ Trial).” BMC Medicine 15 (1): 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-017-0791-y.
- 12. Castaldelli-Maia, João M., Luis E.Segura and Silvia S.Martins. 2021. “The concerning increasing trend of alcohol beverage sales in the U.S. during the COVID-19 pandemic.” Alcohol. Vol 96, Pgs. 37-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2021.06.004
- Johnson, Sara B., Robert W. Blum and Jay N. Giedd. 2009. “Adolescent Maturity and the Brain: The Promise and Pitfalls of Neuroscience Research in Adolescent Health Policy.” The Journal of Adolescent Health: Official Publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine 45 (3): 216-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.05.016.
- Kaur, Harleen, Tushar Singh, Yogesh Kumar Arya and Shalini Mittal. 2020. “Physical Fitness and Exercise During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Enquiry.” Frontiers in Psychology 11 (October): 590172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.590172.
- Li, Ye, Mei-Rong Lv, Yan-Jin Wei, Ling Sun, Ji-Xiang Zhang, Huai-Guo Zhang and Bin Li. 2017. “Dietary Patterns and Depression Risk: A Meta-Analysis.” Psychiatry Research 253 (July): 373-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.04.020.
- Li, Zezhi, Meihua Ruan, Jun Chen and Yiru Fang. 2021. “Major Depressive Disorder: Advances in Neuroscience Research and Translational Applications.” Neuroscience Bulletin 37 (6): 863-80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00638-3.
- Moorman, David E. 2018. “The Role of the Orbitofrontal Cortex in Alcohol Use, Abuse and Dependence.” Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 87 (Pt A): 85-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.01.010.
- Ruiz, Norma A Labra, Daniel SantamarÃa del Ãngel, Hugo Juárez OlguÃn and Miroslava Lindoro Silva. 2018. “Neuroprogression: The Hidden Mechanism of Depression.” Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 14 (October): 2837-45. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S177973.
- Skóra, Maria Nalberczak, Tommy Pattij, Anna Beroun, Georgios Kogias, Dirk Mielenz, Taco de Vries, Kasia Radwanska and Christian P. Müller. 2020. “Personality Driven Alcohol and Drug Abuse: New Mechanisms Revealed.” Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 116 (September): 64-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.06.023.
- Uhl, George R., George F. Koob and Jennifer Cable. 2019. “The Neurobiology of Addiction.” Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1451 (1): 5-28. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13989.
- Vaish, Amrisha, Tobias Grossmann and Amanda Woodward. 2008. “Not All Emotions Are Created Equal: The Negativity Bias in Social-Emotional Development.” Psychological Bulletin 134 (3): 383-403. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.134.3.383.
- van der Valk, Eline S., Mesut Savas and Elisabeth F. C. van Rossum. 2018. “Stress and Obesity: Are There More Susceptible Individuals?” Current Obesity Reports 7 (2): 193-203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-018-0306-y.
- Weir, Kirsten. 2021. “The Extra Weight of COVID-19.” American Psychological Association, Monitor on Psychology; Vol. 52 No. 5 pg. 26. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2021/07/extra-weight-covid.
- Wise, R. A., & Koob, G. F. 2014. “The development and maintenance of drug addiction.” Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, Vol. 39(2), pgs.254-262. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.261
Grace Chung graduated with a B.S. in Biochemistry from Azusa Pacific University in December 2021. She is interested in the integration of science with her Christian faith. She currently works as a referral clinical coordinator at One Legacy (a non-profit, organ procurement organization) in Los Angeles, California.

Leave a Reply